Ports and Adapters¶
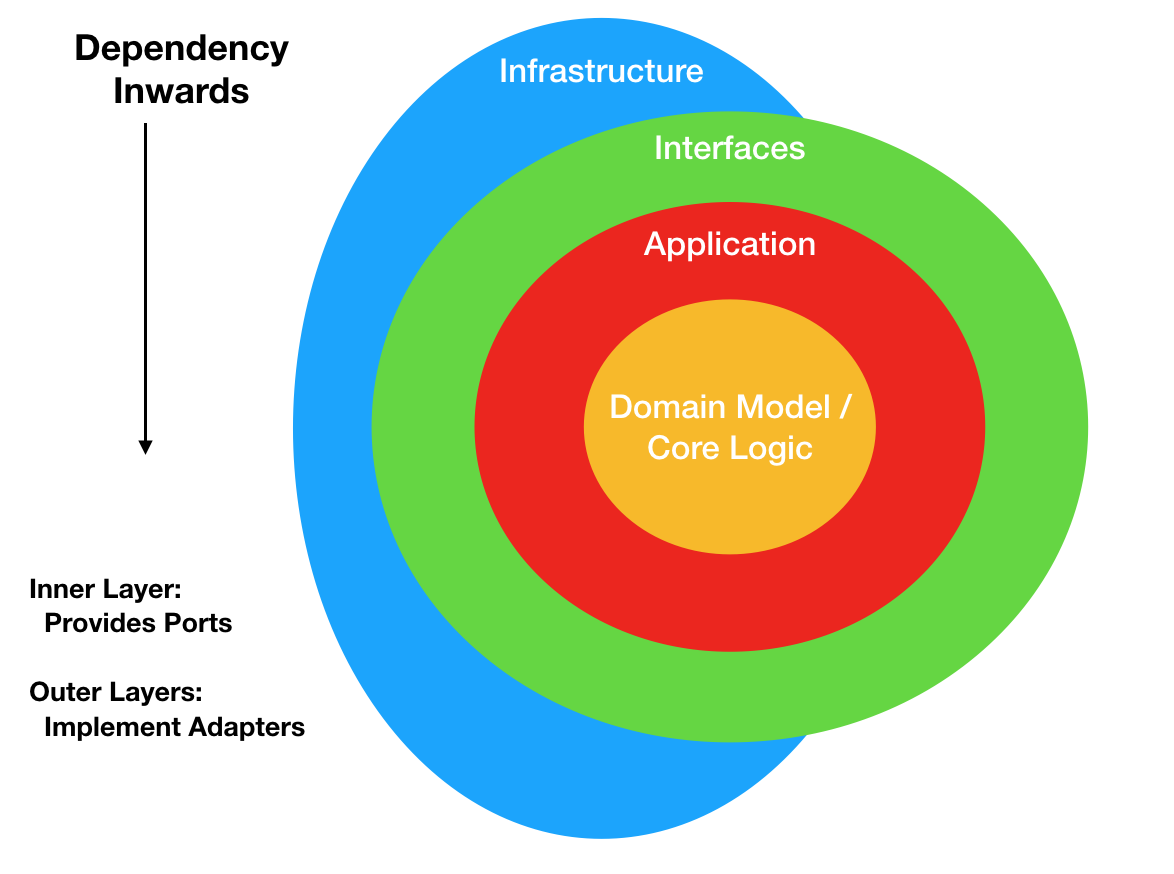
Ports and Adapters is a layering approach that is useful for building maintainable software solutions. It is even consideres by some as "timeless architecture".
Ports and Adapters focuses on building a technology free domain and uses the concepts of primary and secondary ports.
Reade more below or here:
- https://8thlight.com/blog/uncle-bob/2012/08/13/the-clean-architecture.html
- http://www.dossier-andreas.net/software_architecture/ports_and_adapters.html
Layers:¶
The different layers are:
Domain Layer¶
- Technology Free Domain Model
- In Ubiquitous Domain Language
- Potent and easy to understand
Application Layer¶
- Applications API and Services
- Developed around use cases in the application requirements
- This use cases orchestrate the flow of data to and from the entities
- Somehow form the „Application API" (for development)
Interfaces¶
Set of adapters that convert data from the format most convenient for the use cases to the format most convenient for some external agency/access (like Web / DB or in general some outer layer) . This layer contains things like: * web controller / api controller * data transfer objects (dto) or form representations for the external "world"
Infrastructure¶
This layer is where all the details go. The Web is a detail. The database is a detail. We keep these things on the outside where they can do little harm.
This is also where frameworks and tools such as the Database live.
Also the communication with other external systems (APIs) will live here.
Ports and Adapters¶
We are taking the description from http://www.dossier-andreas.net/software_architecture/ports_and_adapters.html
Read is carefully its nice:
-
A port is an entry point, provided. It defines a set of functions.
-
Primary ports (Input Ports) are the main API of the application. They are called by the primary adapters that form the user side of the application. Examples of primary ports are functions that allow you to change objects, attributes, and relations in the core logic. (= MVC)
-
Secondary ports (Data ports) (Interfaces that need to be implemented) =interfaces for the secondary adapters. They are called by the core logic. An example of a secondary port is an interface to store single objects. This interface simply specifies that an object be created, retrieved, updated, and deleted. It tells you nothing about the way the object is stored.
Ports and Adapters in Flamingo¶
Example¶
Lets define a Secondary port inside your domain:
package domain
type (
MyCustomerService interface{
GetCustomer(string) Customer
}
)
Now lets write a Secondary Adapter inside the infrastructure layer
package infrastructure
type (
MyCustomerServiceAdapter struct {
apiClient APIClient
}
)
// verify interface
var _ domain.MyCustomerService = &MyCustomerServiceAdapter{}
func (m *MyCustomerServiceAdapter) GetCustomer() {
//do some stuff with the API
}
// Inject dependency into MyCustomerServiceAdapter
func (svc *GetCustomer) Inject(a APIClient) {
svc.apiClient = a
}
Then bind in your Adapter in the module.go using Dingo:
// Configure DI
func (m *MyModule) Configure(injector *dingo.Injector) {
// ...
injector.Bind(new(MyCustomerService)).To(new(MyCustomerServiceAdapter))
// ...
}